New immune system discovered in bacteria
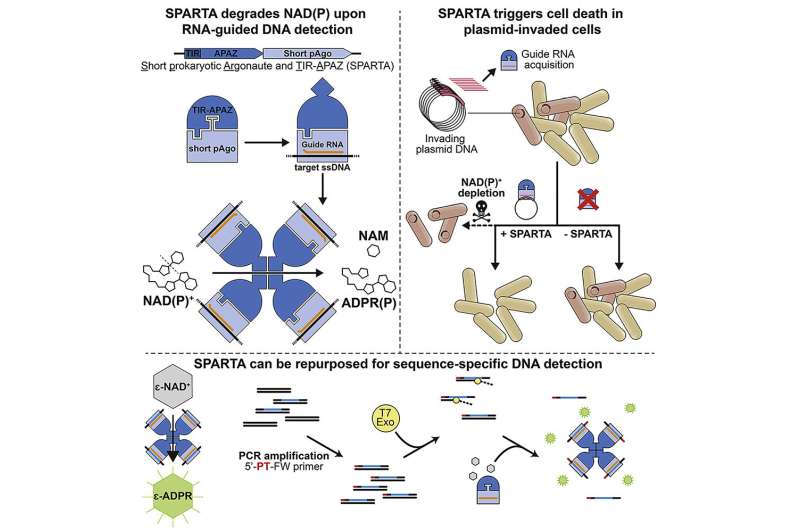
Like people, bacteria have several immune methods to defend from pathogens these kinds of as viruses. These immune systems commonly degrade the DNA of the pathogens to make it harmless. In the investigation team of assistant Professor Daan Swarts from the Laboratory of Biochemistry at Wageningen University & Exploration, an totally new immune method that utilizes one more mechanism for invader neutralization has been found. The findings are revealed in the scientific journal Mobile.
Deep within our physique a constant arms race is using location. On the just one hand, viruses maintain seeking for new techniques to penetrate our cells, and on the other hand, our human body retains coming up with far better protection mechanisms to eliminate these viruses. This is how sickness and overall health are commonly held in equilibrium. The exact arms race is waged involving bacteria and their pathogenic ‘invaders’: viruses and plasmids.
In an article in the scientific journal Cell, Ph.D. candidate Bel Koopal from Daan Swarts’s analysis group describes a new defense system in this arms race. The scientists display that a novel sort of bacterial “Argonaute proteins,” immediately after detecting the invading DNA, intentionally split down all molecules with the eloquent identify nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
Fully shuts down cell
Argonaute proteins come about in multicellular organisms like plants and people, but also in unicellular organisms like micro organism. These Argonautes are programmed with a modest strand of “information RNA” or “guidebook DNA” to obtain invasive RNA or DNA with the exact sequence. In most cases, the intruder is then wrecked by cutting it up into smaller, harmless pieces. Despite the fact that the Argonaute protein in Swarts’s investigation also works by using manual RNA, it defends via a essentially distinctive approach: right after detecting invasive DNA, it wholly shuts down the mobile by breaking down NAD+.
Contaminated cell perishes
The NAD+ molecule has a critical operate in the metabolic process of cells and retains the proverbial engine operating allowing for for the ongoing existence of a mobile. “With no NAD+, the mobile will ultimately die,” Swarts explains. “This might audio contradictory, but it is particularly what is intended to materialize. By permitting the contaminated cell die, the invader are not able to propagate or unfold to neighboring germs. The bacterium mobile is ‘sacrificed’ in purchase to preserve other, healthy cells.”
Innovative germs
This immune technique was observed in distinct species of microbes. Swarts was not stunned that these unicellular organisms have these kinds of sophisticated defense mechanisms. “Persons usually underestimate how able micro organism are,” he claims. “No make a difference how compact microorganisms are, their immune units have been evolving for tens of millions of yrs and become significantly state-of-the-art. They have to, for the reason that the viruses are typically really subtle also.”
“In the foreseeable future, we could possibly be able to detect conditions in the human entire body working with this variety of genetic applications,” observes Daan Swarts.
Swarts, Koopal and their colleagues executed the analysis generally from a scientific need to fully grasp the mechanisms of Argonaute proteins. On the other hand, Swarts believes that these new insights will also have realistic purposes in the very long time period. For example, the investigate group shown that the immune technique can be isolated and subsequently reprogrammed with a strand of guide RNA of preference. As the NAD+ degradation can quickly be detected, the Argonaute protein can be utilised acknowledge specific DNA sequences on command. “In the upcoming, we could be able to detect conditions in the human overall body working with this sort of genetic tools,” Swarts appears ahead. “But we are not there nonetheless. For the time getting, we are enthusiastic by a fundamental curiosity.”
Previous line of defense: How bacterial populations are secured towards viral infections
Balwina Koopal et al, Shorter prokaryotic Argonaute methods induce mobile loss of life on detection of invading DNA, Cell (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.012
Citation:
New immune method discovered in microbes (2022, April 4)
retrieved 7 April 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-04-immune-bacteria.html
This document is topic to copyright. Apart from any good working for the reason of non-public study or study, no
aspect may possibly be reproduced with out the published permission. The articles is supplied for data uses only.






